Identity Access Management (IAM)
Identity Access Management or IAM helps the IT department to provide authenticated access to right individuals and enable authorized access to relevant data within the organization. When it comes to the mobile security for HR Apps, the entire objective behind IAM is to set only one unique identity against one mobile device user. Following are some of the mobile security considerations that are leveraged for IAM.
Role based access
It is very important that access of different features/apps within a HR system is provided based on the role played by an individual within the organization. This can be done by introducing a feature which allows the organization to define roles and linked privileges within the mobile apps. As an example, an employee working as a salesperson in an organization should not have the access rights for master payroll app or engineering teams mobile apps. Apart from this, HR Apps should be smart enough to keep the data within the apps access oriented. By providing limited and required access, the system not only remains more streamlined but also more secure
SSO and Unified Directories
Identity Management App works on the principle of Single Sign On (SSO) which requires the employee to login only once to access all the Mobile Apps like Payroll, Time and Attendance, OnBoard, etc. within the enterprise app store. Mobile apps should be integrated with respective enterprise directories or identity providers like Okta Universal Directory, Azure Active Directory, One Login, etc. for secure login and authentication.
Two Factor Authentication or Multi Factor Authentication (MFA)
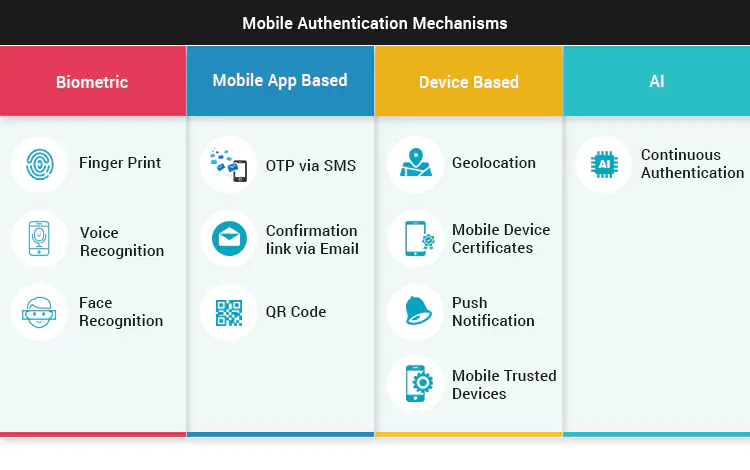
As per Verizon’s 2016 Data Breach Investigation Report, about 63% of confirmed data breaches involved weak, default or stolen passwords. Two factor authentication (2FA) or Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) helps adds additional layer of security above username and password for HR apps to leverage. This can be an biometric authentication, or Smart Credentials using trusted Bluetooth Mobile Devices and many more as stated in below diagram.
Geofencing
Definition of office has now become more flexible with the use of smartphones and laptops. People can access their work from anywhere using any network which makes it easier for attacks. Introducing policies like Geofencing can allow the employees to be more flexible at work while being secure. Geofencing allows the employee to access the apps or software only from certain location say office, home etc. which is to be defined by the company. The location and area restrictions for mobile apps can be implemented by accessing following GPS location or NFC and similar proximity sensors or SIM card number and carrier network info.
Defining security using AI and ML
With more and more mobile devices and flexible work environment, hackers now have multiple ways to intrude enterprise network and access sensitive information through millions of mobile devices that can be compromised. AI and ML presents significant potential to record and track suspicious behavior using pattern matching and proven data models to predict threat well in advance of an uncompromised event.
Mobile presents ease of logging user-activities in the cloud. This is further supported with data from communication standards used within emails, volume and type of files being shared, work dynamics throughout the organization using digital footprints of its employees etc. Detecting pattern using such data helps create machine learning models to identify standard and unusual behavior within the network. Unusual behaviors can be any of the above-mentioned examples like logging in from a different location, trying to tamper 2FA and MFA, attempt for unauthorized access, addition of fake employees, emails requesting sensitive information from some unauthorized sources etc. Google’s Chronicle, Darktrace are few of the examples which have already incorporated AI and MLP to track unusual activities.
To conclude, predicting network threats and fraudulent use-cases using AI & ML is essential to strengthen mobile security for HR mobile apps. Furthermore, it is imperative to implement enterprise SSO and multi-layer authentication in HR mobile apps by leveraging native mobile-based identity solutions. Lastly as explained in previous blog, ensuring right policies for mobile device management and secured access to both enterprise apps and data will ensure tighter control and relief to IT department while continuing to support mobile enabled HR use-cases.